Motor cortex
Last updated on
2022-09-07
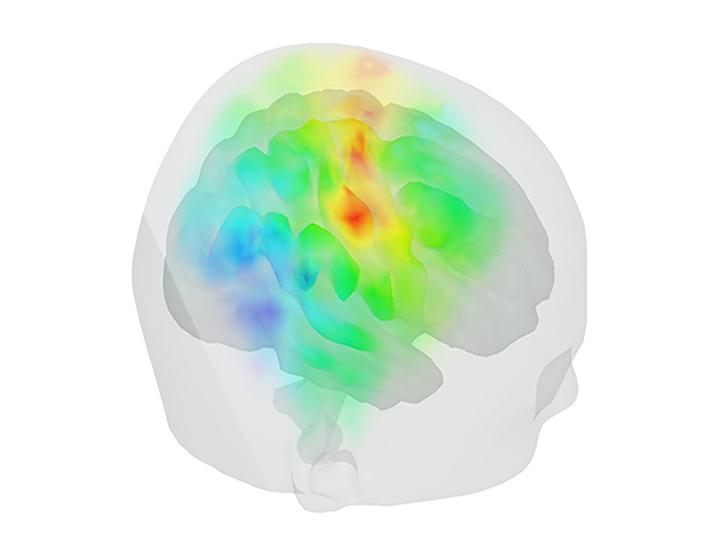
fNIRS stands for functional near infrared spectroscopy. The functional component comes from the fact that our fNIRS devices are capable of assessing brain activity. This is done by measuring changes in oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin, which reflect local brain activity. Moreover, fNIRS provides a non-invasive manner to achieve an excellent resolution brain signal in real-time.
Publications
Parkinson’s disease patients show delayed hemodynamic changes in primary motor cortex in fine motor tasks and decreased resting-state interhemispheric functional connectivity: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study
Significance People with Parkinson’s disease (PD) experience changes in fine motor skills, which is viewed as one of the hallmark signs …
Brain activation associated with low‐ and high‐intensity concentric versus eccentric isokinetic contractions of the biceps brachii: An textlessspan style="font-variant:small-caps;"textgreaterfNIRStextless/spantextgreater study
Abstract Studies have shown that neural responses following concentric (CON) and eccentric (ECC) muscle contractions are different, …
C-STIM: Protocol for a randomized, single-blind, crossover study of cerebellar repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) for postural instability in people with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP)
Background Methods for modulating the cerebellum with transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) are well established, and preliminary …
Near-infrared spectroscopy - electroencephalography-based brain-state-dependent electrotherapy: A computational approach based on excitation-inhibition balance hypothesis
Stroke is the leading cause of severe chronic disability and the second cause of death worldwide with 15 million new cases and 50 …
Simultaneous measurements of cerebral oxygenation changes during brain activation by near-infrared spectroscopy and functional magnetic resonance imaging in healthy young and elderly subjects
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) and functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) both allow non-invasive monitoring of cerebral …
<title>Detailed evidence of cerebral hemoglobin oxygenation changes in response to motor cortical activation revealed by a continuous-wave spectrophotometer with 10-Hz temporal resolution</title>
In the last four years near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) has been used in cerebral functional activation studies to monitor changes in …